Introduction
Medical billing is the administrative process of patient registration of translating healthcare services into claims that insurance companies can pay. Medical billing doesn’t involve medical procedures or clinical tasks; instead, it focuses on handling paperwork, payments, and communication with insurance providers.
Medical billing is in high demand due to the growing healthcare industry, increased insurance utilization, and the need for skilled professionals to accurately manage insurance claims.
Professionals remain employed in the field, reflecting strong job satisfaction and demand. Healthcare coding and billing directly impact the financial stability of a healthcare practice.
This career is ideal for:
- Beginners who are just starting their careers
- People looking for remote or work‑from‑home opportunities
- Career changers seeking a stable, entry-friendly role
- Individuals who enjoy computer-based administrative work
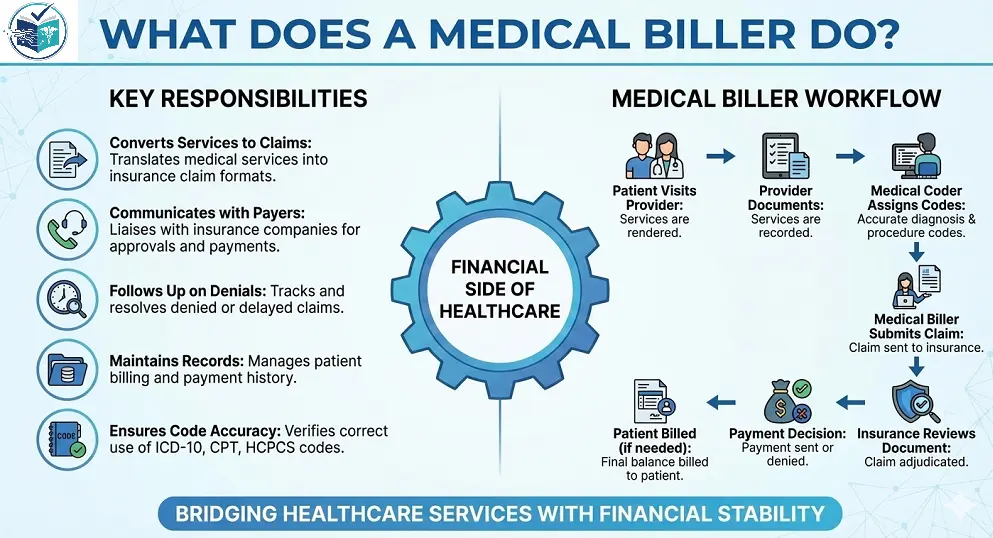
What Does a Medical Biller Do?
A medical biller handles the financial side of the health care organization. A medical biller’s responsibilities are as follows:
- Converting medical services into insurance claims.
- They communicate with insurance companies for approvals and payments.
- They do follow-ups on denied or delayed claims.
- They are responsible for maintaining patient billing and payment records.
- They ensure that correct medical codes (like ICD-10, CPT, HCPCS) are used.
Medical Biller Workflow:
- Patient visits provider → Provider documents the services that he performed → Medical coder assigns codes accurate to those diagnoses → Medical biller submits the claim → Insurance company reviews the document → They decide whether to send the payment or not → Patient billed if needed.
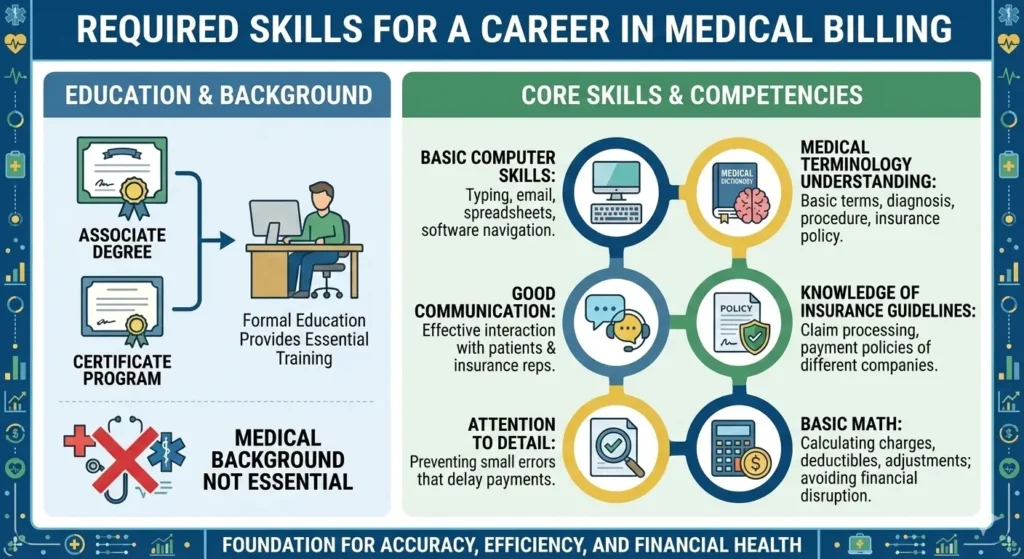
Required Skills for Medical Billing
Starting a career in medical billing and coding begins with obtaining the right education. Most professionals move forward with either an associate degree or a certificate program, which provides essential training in the core areas of the field. Medical Billing does not essentially require a medical background, but the core skills involved are:
- Basic computer skills: individuals should have basic typing, email, spreadsheet, and software navigation skills.
- Understanding of medical terminology: they should understand the basic terms like diagnosis, procedure, and insurance policy
- Good communication: soft communication and talking to patients and insurance representatives is necessary.
- Knowledge of insurance guidelines: must have a basic understanding of how different companies process claims and their payment policies.
- Attention to detail: Small errors can delay payments, so attention to detail is required
- Basic math: individuals must know about calculating charges, deductibles, and adjustments; a minor error may lead to financial disruption.
These skills can be learned by anyone with practice and training. The most important ingredient is dedication.
Eligibility & Education Requirements
Medical billing is a beginner-friendly skill. Individuals can start their journey through simple education:
- A high school diploma or equivalent is often the only mandatory requirement.
- Optional certificate programs can boost job readiness.
- Optional medical billing courses can be done online from the comfort of your room or in person.
- Apprenticeships or entry-level jobs are ideal for gaining experience without certification.
Many employers hire beginners as long as they show a willingness to learn and are energetic to do the job.
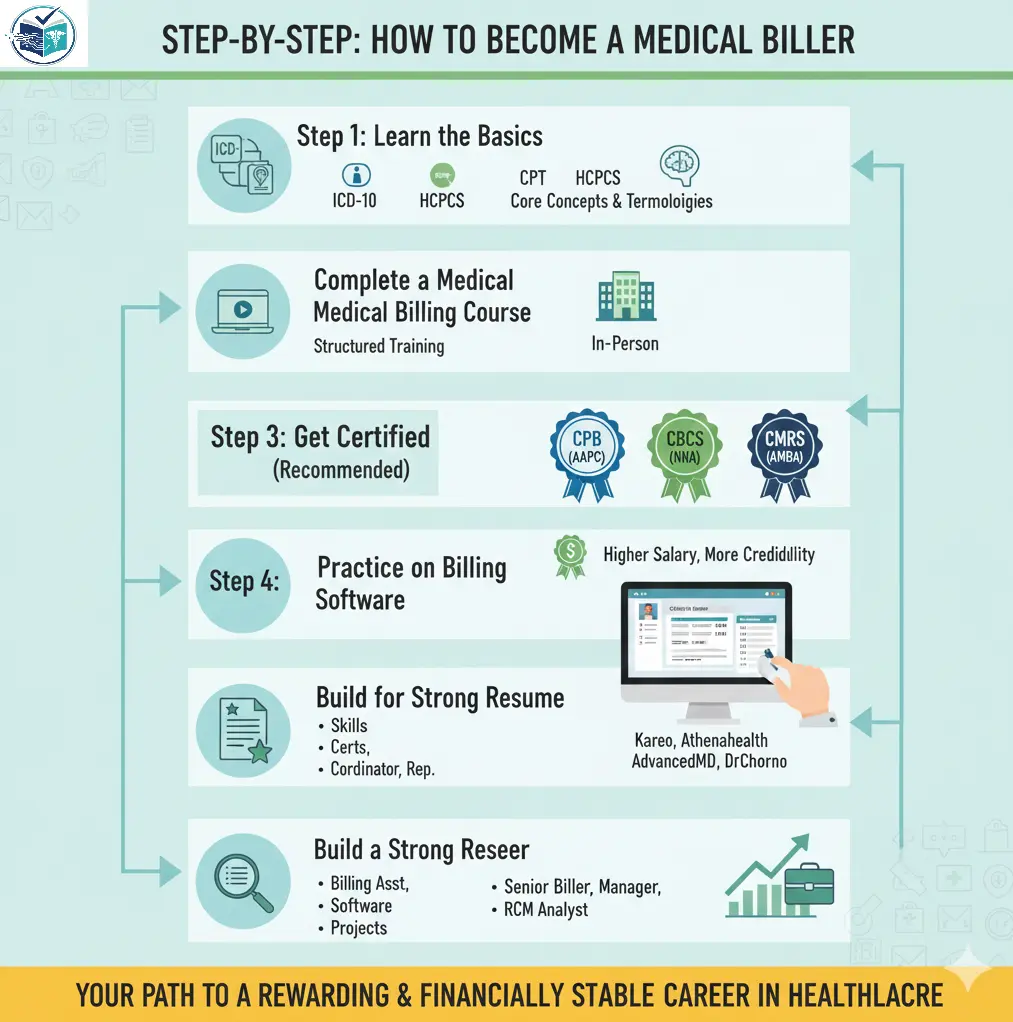
Step-by-Step: How to Become a Medical Biller
A series of steps must be followed to become a Medical Biller. We will break down these steps for our easy understanding and to fully grasp these concepts.
These steps include:
Step 1: Learn the Basics of Medical Billing
Start by learning the core concepts of Medical Billing, like:
- How insurance claims are made and how their payments are made. A Medical Biller should have a complete understanding of how claims are made and how providers get paid for their services. They should learn what coding is, why it matters, and what type of documentation is required by insurance companies.
Key terminologies to learn for becoming a Medical Biller:
- ICD-10: Diagnosis codes
- CPT: Procedure and service codes
- HCPCS: Supplies, equipment, additional codes
Basic insurance rules include understanding Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers.
Step 2: Complete a Medical Billing Course
An individual seeking to become a Medical Biller can choose any format of courses depending on their budget and their preferred learning style. Either they want to do online courses or in-person courses.
Several types of courses are:
- Free online courses: These are good for basic understanding.
- Paid certificate courses: They provide structured learning and hands-on training.
- Self-paced programs: These are ideal for busy individuals who prefer flexible learning.
Step 3: Get Certified (Optional but Recommended)
Popular certifications of medical billing include:
- CPB – Certified Professional Biller (AAPC)
- CBCS – Certified Billing and Coding Specialist (NHA)
- CMRS – Certified Medical Reimbursement Specialist (AMBA)
Benefits of certification
- Certified individuals have higher salary potential as medical billers.
- Faster chances of getting hired. Individuals with certifications are preferred over those without them.
- More credibility on your resume. Certificates improve the individual’s credibility.
Step 4: Practice on Billing Software
Beginners aiming to secure a position as medical billers should focus on learning basic software functions.
Popular medical coding platforms include:
- Kareo
- Athenahealth
- AdvancedMD
- DrChrono
These are the practice areas on which beginners should focus:
- Entering patient information so they can avoid errors.
- Practicing on how to create and submit claims and how to make approval-ready claims.
- Posting payments and adjustments.
- Efficient communication.
Step 5: Build a Strong Resume
For building a strong resume, individuals include these details
- Skills they learned, like coding terms, billing cycle knowledge, or any related skills.
- Course certificates that individuals earned.
- Software knowledge.
- Include any small projects or practice exercises performed during certification.
Step 6:Apply for Entry-Level Positions
For applying to an Entry-Level Position, individuals should search for jobs titled as
- Medical Biller
- Billing assistant
- Billing Coordinator
- Patient Account Representative
Freshers should apply even if they don’t meet each and every requirement of the job description; beginners are commonly hired.
Step 7:Grow your career
After gaining experience as a Medical Biller. Individuals should start applying for higher positions once they are accustomed to the specific work environment.
Career advancement options to look for are:
- Senior Medical Biller
- Billing manager
- Coding Specialist
- Revenue Cycle Analyst
This field has a long-term growth potential. If an individual plans to stay in the field of Medical Billing, they can earn a pretty handsome amount from it
Salary Expectations
Below is a simple example of salary Ranges which Medical Billing has to offer:
| Position | Experience | Average Salary |
| Entry-level Biller | 0-1 year | $32000-$38000 |
| Certified Biller | 1-3 years | $40000-$52000 |
| Senior Biller | 4+ years | $55000-$65000 |
Salaries also depend upon location, employer, and certifications.
Individuals are advised to read job descriptions thoroughly to know what the job has to offer and what role it requires an individual to play.
Work-From-Home Medical Billing
Many healthcare companies and organizations now offer work-from-home. Remote Billing roles are becoming common and more popular due to their flexibility and ease, especially among students, parents, and part-time workers.
A Medical Biller working from home must show:
- Independent working abilities, i.e., Medical Billers, need to ensure that they are capable of handling things without direct supervision.
- Strong communication to speed up the reimbursement process.
- Accuracy and Discipline play a key role in defining a Biller’s capabilities, as even minor errors may lead to claim denials or may result in delayed payments from insurance providers.
Common Mistakes Beginners Should Avoid:
Beginners should pay more attention to details in order to keep their job smooth and steady, and they should avoid the mistakes listed below:
- Not paying proper attention to learning payer guidelines and insurance guidelines.
- Depending only on theoretical concepts instead of hands-on practice.
- Not maintaining proper documentation records. This may lead to a financial imbalance of an organization.
- Failing to follow up on denied claims and not being able to keep up with AR Follow-ups.
Learning from these mistakes early improves an individual’s efficiency. While ignorance of these mistakes can prove fatal to the job itself.
Final Tips & Conclusion
To begin your career as a Medical Biller, you must focus on:
- Taking a good course for improved certification
- Do not rely on theoretical tasks, but practice daily to have hands-on experience
- Applying for jobs even if you feel nervous and think that you do not have the full-fledged skills
- Building confidence through small training tasks to boost your confidence for when you actually step into the real field.
- Medical billing is a solid and beginner-friendly career choice with growth, stability, and remote opportunities. With consistent practice and the right steps, you can start your journey even with no experience.
Is medical billing hard to learn?
It’s a pretty beginner-friendly skill to learn. It just needs the right training and a bit of hard work.
Can I become a Medical Biller without experience?
Yes, many employers are ready to hire freshers. They also provide early training to the freshers.
How long does it take to learn medical billing?
The duration necessarily depends upon the certifications (i.e. usually takes up to 2-6 months)
Is certification required to get a job?
Not essentially but it is highly recommended to get one.
Can I do medical billing from home?
The answer is yes, many remote medical billing jobs are available in the industry.
Which is better: billing or coding?
Billing is an administrative process. Coding is a more technical process.
Both have growth opportunities
What software do medical billers use?
The most common software used is
Kareo, Athenahealth, AdvancedMD, and DrChrono
Do medical billers interact with patients?
Yes, they do communicate with patients. This communication usually involves procedure price quotations or related questions.
Is medical billing a good career in 2025?
Yes, it’s a stable and growing field. It has much to offer to the individuals associated with it.
How much do beginners earn?
Beginners earn around $32000-$38000 per year on average.
Helpful Resources/References
- AAPC. (2024). Certified Professional Biller (CPB) certification guide. AAPC.
https://www.aapc.com - Burks, K., Shields, J., Evans, J., Plumley, J., Gerlach, J., & Flesher, S. (2022).
A systematic review of outpatient billing practices. SAGE Open Medicine, 10.
https://doi.org/10.1177/20503121221099021 - Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. (2024).
Medicare billing: 837P and Form CMS-1500 instructions. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services.
https://www.cms.gov - Faizo, A. L. A., Ali, H. A. A., Alonezi, T. A. I., Albarqi, F. A. A., Allahji, S. A. S.,
Alseqamy, A. M. A., Alhaity, K. M. S., Alnami, A. Q. A., Alkhabbaz, N. K. E.,
Aljeddawi, H. M. A., Alburayh, S. H., Albarrak, M. M. A., & Alwane, M. N. A. (n.d.).
The impact of accurate medical coding on healthcare quality and patient safety: A systematic review.
https://doi.org/10.70082/jm2xk804 - Bouchrika, I. (2026).
How to become a medical biller & coder in Rhode Island.

About the Author
Laim Will is a medical billing and coding content writer with 5 years of practical experience in Revenue Cycle Management (RCM). She specializes in creating beginner-friendly medical billing guides, denial management explanations, coding basics, and AR workflow insights. Her content is designed to simplify complex billing processes using real-world industry knowledge and clear explanations.




