Beyond the Sticker: The reality behind the medical billing software is really stark; the price you normally see at the front is just the tip of the iceberg. A published monthly rate of any medical software may seem affordable at first, but once you include the software’s setup fee, its usage, denial rates, and other hidden charges, the price may increase significantly.
Return on investment (ROI) is a strategic move. For example, if you purchase a billing solution that costs around $500 per month, and by using that software’s tool, your claim denials have been reduced significantly, this choice will be your best choice rather than using software that claims to be “free,” but that software is unable to diagnose any underlying issue in your management.
In this guide, we will break down the primary pricing models and reveal hidden costs that raise the price, and we will provide you with clear, actionable steps by which you will be able to calculate the true ROI on your investment.
Primary Pricing Models:
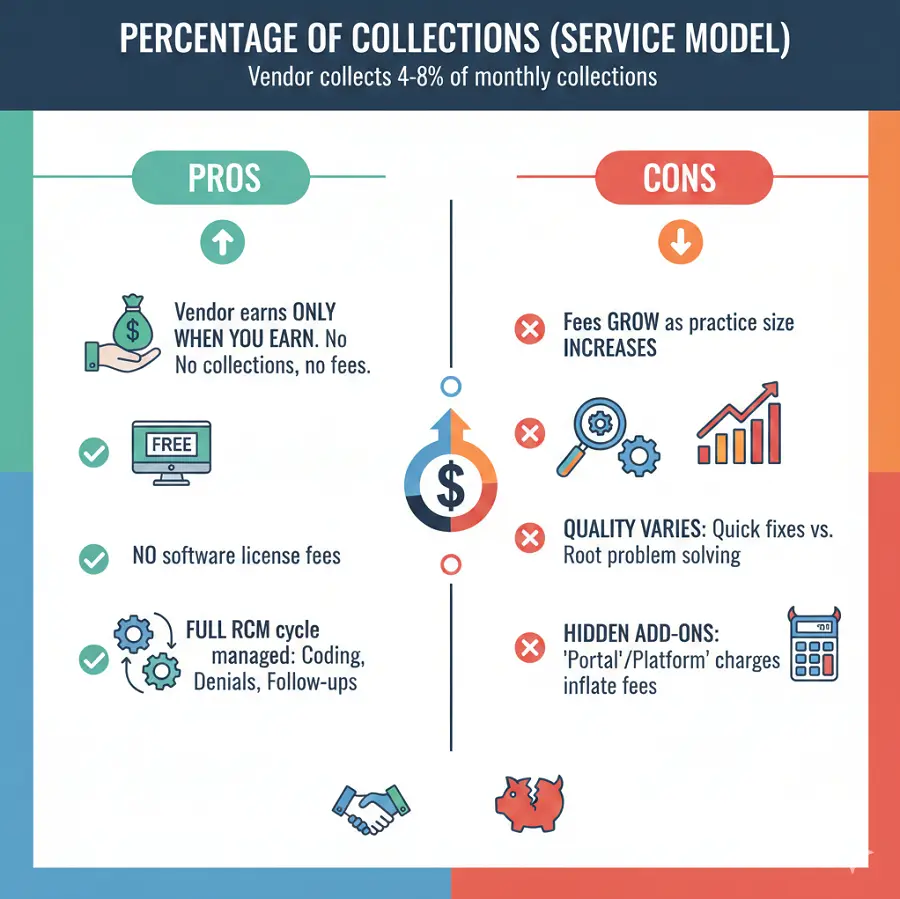
Percentage of Collections (Service Model)
In this model, a vendor collects the percentage of the claims collected on your behalf. Those collection rates are usually 4-8% of monthly collections.
Pros:
Vendors earn only when you earn. If your practice was unable to collect even one insurance, then there is no need to worry; your vendor can not charge you a single penny.
Your practice does not have to pay any software license fee or anything like that.
As the full RCM cycle is managed by vendors, usually they are the ones performing coding, denial management,, and follow-ups.
Cons:
Over time, as the practice grows in size, so do the subscription fees.
Quality of work varies from vendor to vendor; some vendors may prioritize quick fixes while others believe in eradicating the problem from its very root.
Hidden add-ons are the biggest upset of billing software; they may add charges under the name of “portal” or “platform“ charges. They may seem insignificant to you at the start, but these little devils cause a surge in the subscription fee.
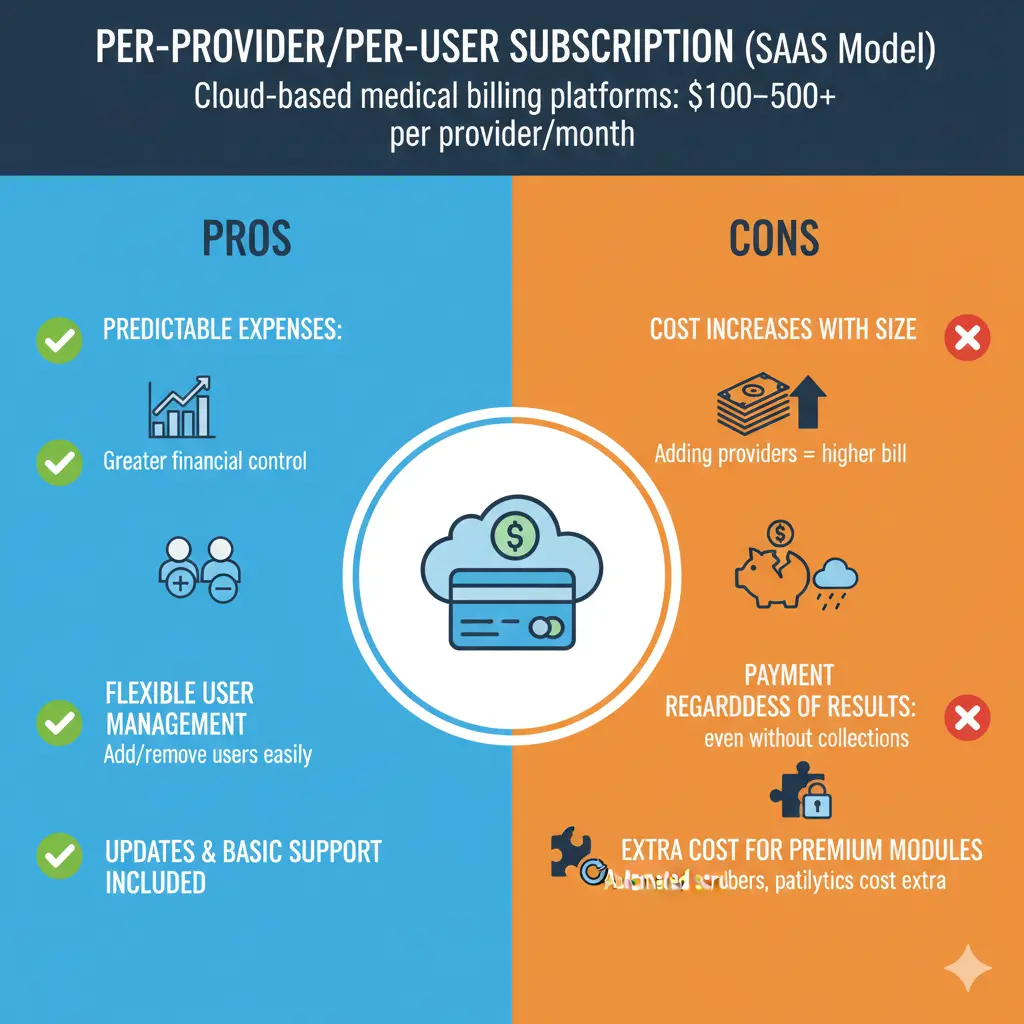
Per-Provider/Per-User Subscription (SaaS Model)
This is the most common model of medical billing. In this model, you pay monthly subscription fees and purchase access to medical billing software. Cloud-based medical billing platforms usually range from $100 to $500+ per provider per month.
Pros:
With this module, you get more predictable expenses, so you have greater control over your finances.
You can add or remove users as per your requirement. Usually, all the updates or basic support are provided in the plans.
Cons:
Even though this model gives you the option to add or remove providers, adding a provider results in an increased bill.
You need to pay the subscription fees, even if you do not get the desired results.
Modules like automated claim scrubbers, patient portals, or analytics often come with extra cost. (Software Finder)
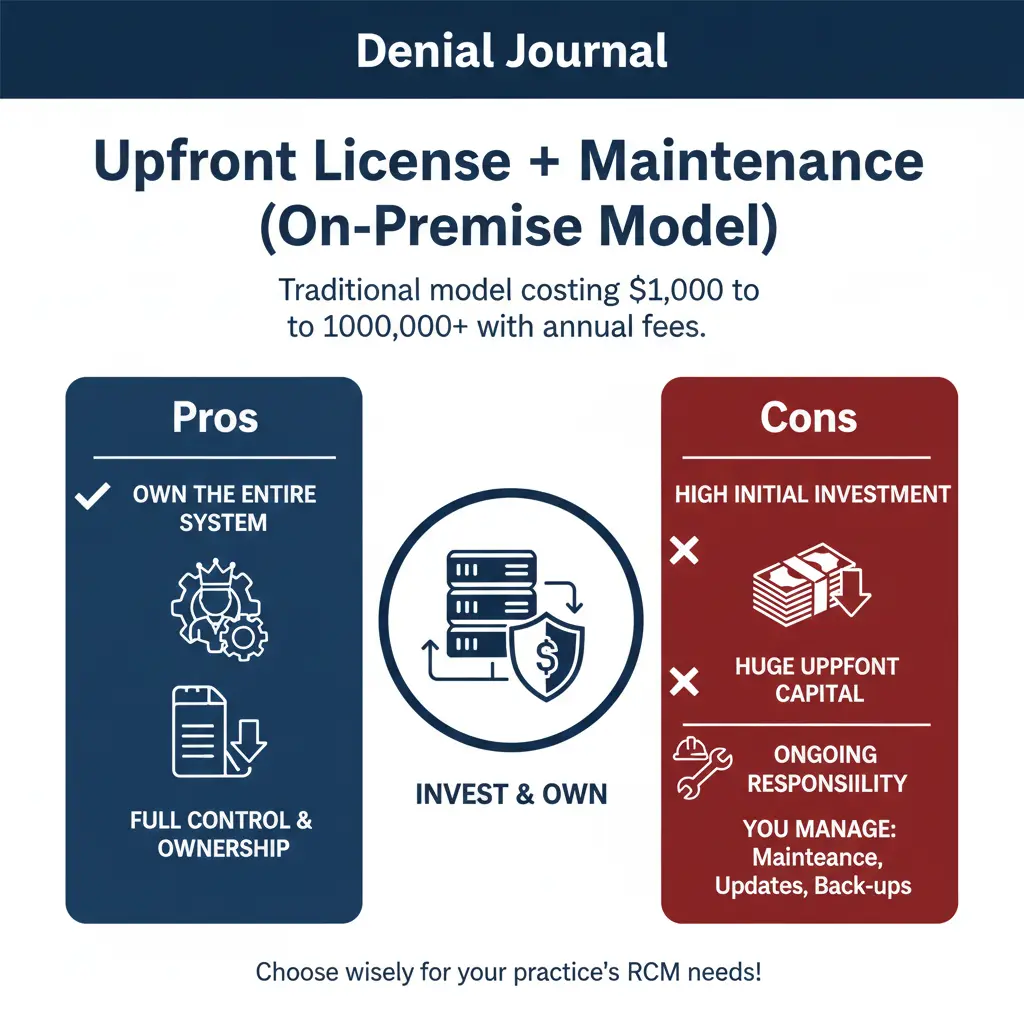
Upfront License + Maintenance (On-Premise Model)
The on-premise model is a traditional and quite expensive model; it requires a huge amount of capital to purchase the software and license. These systems may cost up to $10,000 to $100,000+, with annual maintenance and upgrade fees thereafter.
Pros:
You own the whole software system, but remember that with great power comes great responsibility.
Cons:
You need to invest a huge sum of money with no benefits in sight.
The practice is responsible for any maintenance costs, updates, or backup costs.
Hopefully, these insights will help you make a well-informed decision when choosing the right RCM model.
Revealing the Hidden Costs
Even the best-priced medical billing software can add up hidden costs or charges that may cause a surge in the monthly subscription fees. Below, we will discuss several types of fees or charges that are incurred in RCM software.
- Implementation & Setup Fees:
Many vendors charge a one-time fee for the setup of the software. These fees vary from hundreds to thousands of dollars.
- Data Migration Fees:
Transferring of older data, such as patient demographics, payer lists, and claims history, often costs an extra dime.
- Training Fees:
Making the staff well acquainted with the new software also adds to the cost.
- Clearinghouse & Transaction Fees:
Electronic data interchange (EDI) receiving electronic remittance advice (ERA) can significantly inflate the cost.
- Support and Maintenance Fees:
Annual renewal cost or tiered support cost can add unexpected expenses.
- Regulatory Update Fees:
Software compliance updates (e.g., CPT/ICD changes) may be included in SaaS updates, but can be extra with older or on-premise systems.
If you are planning to buy billing software and you do not take these hidden costs into account, then I feel sorry to inform you that these costs will inflate the TCO far beyond the quoted price.
Calculating True ROI:
Step 1: Calculate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Use a simple formula to calculate TCO
TCO = Upfront Fees + (Annual Subscription × Number of Years) + Hidden Fees
Step 2: Quantify Revenue Gain (The Savings)
Identify the key improvements done by the software or services, like;
- Reduction in Denials
- Faster Reimbursement
- Staff Efficiency
Step 3: Calculate ROI:
A standard ROI metric is
Positive ROI means your investment not only paid for itself but also contributed additional net revenue.
Conclusion and Next Steps
The value of medical billing software is not solely measured by its pricing model but also by its ability to reduce claim denials, accelerate cash flow, and streamline the operations. The higher cost of medical billing software can be justified if its ROI is highly positive.
Next Steps:
Then compare software vs. outsourcing models and decide which one is better for you based on your practice’s size and workflow needs.
Begin your journey of finalizing medical billing software by simply requesting vendors for their cost sheets.
Calculate your claim denial rates and how many days it takes your practice to recover accounts receivable (AR).
Calculate ROI by using the above-provided framework.
References
Accurate Billing Systems. How much does medical billing software cost in 2025 for healthcare providers? Published 2025. Accessed January 9, 2026. https://www.accuratebillingsystems.com/474-how-much-does-medical-billing-software-cost-in-2025-for-healthcare-providers
PriceItHere. How much does medical billing software cost in 2025? Published 2025. Accessed January 9, 2026. https://priceithere.com/medical-billing-software-prices/
Bouchrika I. Best billing software for healthcare for 2026. Published 2026. Accessed January 9, 2026. https://research.com/software/billing-software-for-healthcare
PureDI. RCM software pricing comparison. Published 2025. Accessed January 9, 2026. https://puredi.com/blog/rcm-software-pricing-comparison
BristolHCS. Hidden costs to watch for in medical billing software. Published 2025. Accessed January 9, 2026. https://www.bristolhcs.com/blog/blog-detail/hidden-costs-to-watch-for-in-medical-billing-software-what-practices-often-overlook
US Department of Health & Human Services. HIPAA audit program protocol. Updated December 2024. Accessed January 9, 2026. https://www.hhs.gov

About the Author
Laim Will is a medical billing and coding content writer with 5 years of practical experience in Revenue Cycle Management (RCM). She specializes in creating beginner-friendly medical billing guides, denial management explanations, coding basics, and AR workflow insights. Her content is designed to simplify complex billing processes using real-world industry knowledge and clear explanations.




